Cloud Computing Infrastructure for HPC
Any Architecture, Any Cloud, Worldwide
Instant access to the world’s latest high-performance computing architectures, from anywhere in our global cloud provider network.
- Preconfigured coretypes simplify finding the right architectures
- Use any architecture from our global multi-cloud network
- Successful job completion guarantee backed by SLA
Broad Set of High Performance
Computing Architectures
CPU
Intel Xeon Skylake, Phi, Broadwell
AMD EPYC
Xilinx FPGA
GPU
NVIDIA Volta V100
NVIDIA Tesla P100
NVIDIA Tesla K80
NVLink
Memory
3.2-3.10 GB/core
up to 2TB/server
Interconnect
Low latency 10 GigE, 25 GigE and Infiniband
Storage
Solid State Disks (SSD) 15-400 GB/core or unlimited




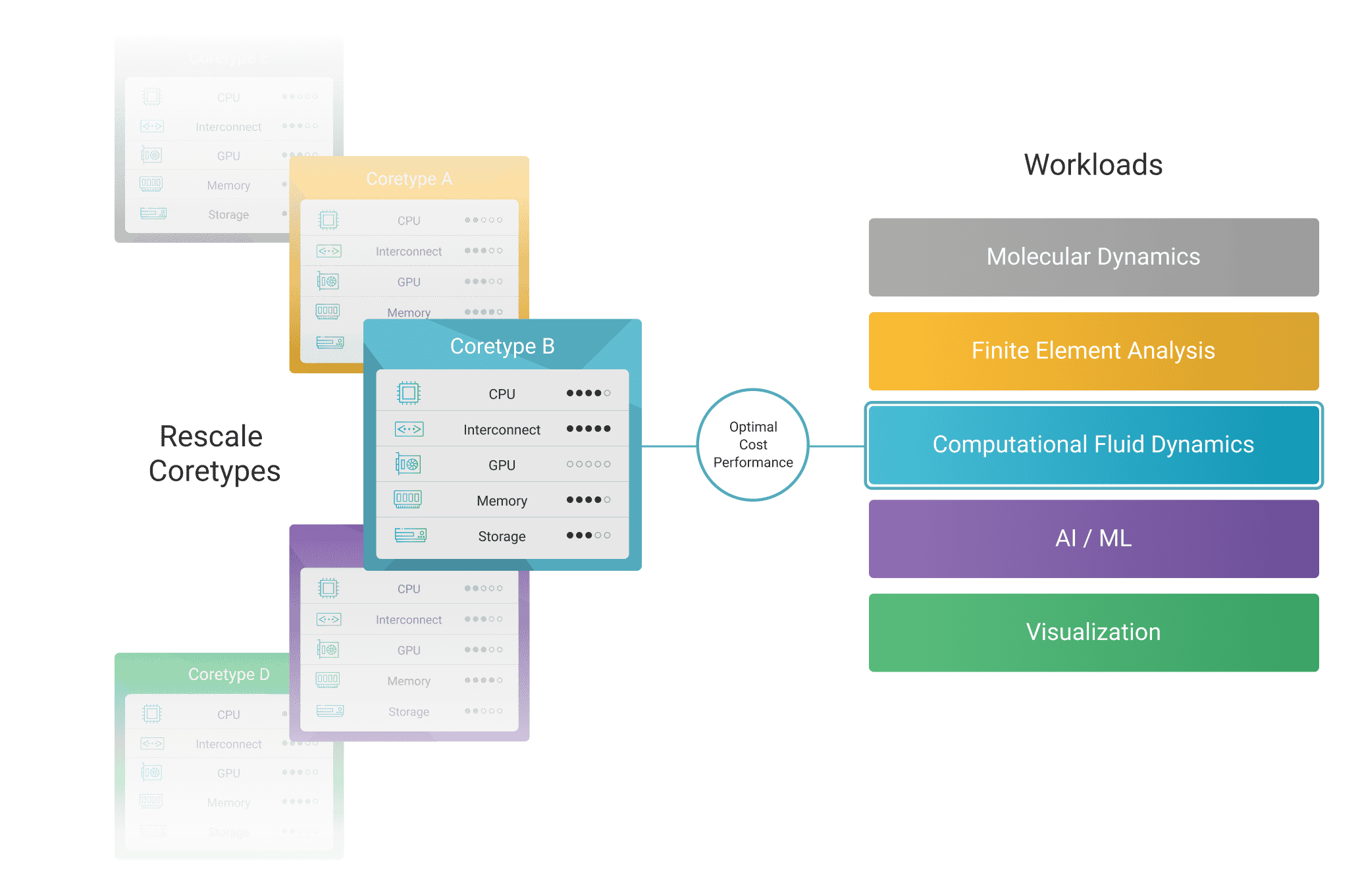
Rescale Coretypes
Simplify finding the right hardware architecture and configuration with
predefined coretypes optimized for each workload.
Find out the best Rescale coretype for your applications:
Coretype Portfolio
The latest high performance computing architectures available on Rescale’s global cloud provider network.
| Primary Coretypes | Memory (GB/Core) | Network IO | Storage (GB/Core) | Processor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose (30) | ||||
| Andalusite | 8 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Antimony | 8 | 10.0 | 18 (SSD) | AWS Graviton2 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| Caesium | 16 | 200.0 | 237 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Calcite | 8 | 30.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8272CL (Cascade Lake) |
| Calcite v2 | 8 | 35.0 | 75 (SSD) | 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Platinum 8370C (Ice Lake) |
| Calyptolite | 4 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) |
| Emerald | 4 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum P-8124 (Skylake) |
| Emerald Max | 4 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum P-8124 (Skylake) |
| Ferrite | 4 | 10.0 | 16 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8168 (Skylake) |
| Ferrite Max | 4 | 10.0 | 16 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8168 (Skylake) |
| Gallium | 4 | 10.0 | 18 (SSD) | AWS Graviton2 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| Hickory | 4 | 50.0 | 31 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa |
| Jacinth | 4 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Kyanite | 8 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Luna | 4 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Cascade Lake) |
| Luna Max | 4 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Cascade Lake) |
| Moissanite | 8 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Palladium | 4 | 25.0 | 18 (SSD) | AWS Graviton2 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| Palladium Max | 4 | 25.0 | 18 (SSD) | AWS Graviton2 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| Pectolite | 2 | 200.0 | 18 (SSD) | AWS Graviton3 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| Redbud | 2 | 50.0 | 36 | AMD EPYC (Genoa) |
| Ruby | 16 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Sitka | 16 | 30.0 | 32 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7452 (Rome) |
| Spinel | 4 | 40.0 | 8 | Intel Xeon IceLake |
| Spruce | 8 | 30.0 | 16 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7452 (Rome) |
| Spruce v2 | 8 | 32.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation AMD EPYC 7763v |
| Starlite | 4 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Starlite Max | 4 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Tantalum | 16 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Zeolite | 4 | 10.0 | 18 (SSD) | AWS Graviton3 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| High-Speed Interconnect (47) | ||||
| Albite | 28 | 200.0 | 120 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Amber | 4 | 100.0 | 11 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7551 (Naples) |
| Amber v2 | 4 | 200.0 | 8 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7742 (Rome) |
| Ammonite | 4.3 | 200.0 | 8 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7742 (Rome) |
| Andalusite | 8 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Apatite | 5.45 | 200.0 | 10 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7742 (Rome) |
| Aventurine | 16 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Balsam | 8 | 100.0 | 12 | AMD EPYC (Genoa) |
| Caesium | 16 | 200.0 | 237 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Calyptolite | 4 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) |
| Carbon | 8 | 100.0 | 15 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8168 (Skylake) |
| Catseye | 5.25 | 100.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum P-8124 (Skylake) |
| Catseye Max | 5.25 | 100.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum P-8124 (Skylake) |
| Cedar | 4 | 100.0 | 12 | AMD EPYC (Rome) |
| Cuprite | 32 | 400.0 | 150 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Cuprite High Memory | 59 | 400.0 | 150 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Cypress | 5.3 | 100.0 | 16 | AMD EPYC (Milan) |
| Deodar | 16 | 100.0 | 48 | AMD EPYC (Milan) |
| Edenite | 14 | 200.0 | 60 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Elm | 4 | 100.0 | 12 | AMD EPYC (Milan) |
| Fir | 8 | 100.0 | 24 | AMD EPYC (Milan) |
| Fordite | 16 | 400.0 | 75 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Fordite High Memory | 29 | 400.0 | 75 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Graphite V2 | 16 | 100.0 | 1250 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Skylake) processors |
| Hematite | 7 | 200.0 | 30 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Hickory | 4 | 50.0 | 31 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa |
| Jacinth | 4 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Jasper | 7.1 | 200.0 | 16 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7742 (Rome) |
| Juniper | 5.33 | 100.0 | 16 | AMD EPYC (Rome) |
| Limonite | 4.67 | 200.0 | 20 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Linden | 4 | 100.0 | 12 | AMD EPYC (Genoa) |
| Moissanite | 8 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Mulberry | 32 | 100.0 | 48 | AMD EPYC (Genoa) |
| Natrolite | 8 | 400.0 | 37 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Natrolite High Memory | 15 | 400.0 | 37 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Peridot | 10.91 | 200.0 | 21 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7742 (Rome) |
| Poplar | 16 | 100.0 | 24 | AMD EPYC (Genoa) |
| Pyrite | 8 | 100.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) Processors |
| Pyrite Max | 8 | 100.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) Processors |
| Rozenite | 3.75 | 200.0 | 16 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Siderite | 5 | 400.0 | 25 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Siderite High Memory | 10 | 400.0 | 25 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Tantalum | 16 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Tenorite | 4.36 | 400.0 | 20 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Tenorite High Memory | 8 | 400.0 | 20 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Tsavorite | 14.2 | 100.0 | 98 (SSD) | Bare Metal - Intel Icelake |
| Yttrium | 10.66 | 100.0 | 164 (SSD) | Bare Metal - Intel Xeon Gold 6154 (Skylake) |
| Large Memory (41) | ||||
| Albite | 28 | 200.0 | 120 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Aventurine | 16 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Chromium | 15.75 | 30.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8272CL (Cascade Lake) |
| Chromium v2 | 16 | 35.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Platinum 8370C (Ice Lake) |
| Cuprite | 32 | 400.0 | 150 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Cuprite High Memory | 59 | 400.0 | 150 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Diamond | 16 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8151 |
| Edenite | 14 | 200.0 | 60 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Fluorite | 30.5 | 25.0 | 117 (SSD) | 16 nm Xilinx UltraScale Plus FPGA with Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Fordite | 16 | 400.0 | 75 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Fordite High Memory | 29 | 400.0 | 75 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Graphite | 15.25 | 25.0 | 475 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Graphite V2 | 16 | 100.0 | 1250 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Skylake) processors |
| Quartz | 15.25 | 20.0 | 400 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 (Ivy Bridge) |
| Gold | 15.25 | 10.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 (Ivy Bridge) |
| Karlite | 64 | 100.0 | 32 | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Cascade Lake) |
| Karlite Metal | 64 | 100.0 | 32 | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Cascade Lake) |
| Malachite | 16 | 50.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Moonstone | 16 | 25.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Moonstone Max | 16 | 25.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Natrolite High Memory | 15 | 400.0 | 37 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Oak | 16 | 20.0 | 36 | AMD EPYC 7000 series |
| Pearl | 14 | 10.0 | 192 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5 v3 (Haswell) |
| Peridot | 10.91 | 200.0 | 21 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7742 (Rome) |
| Prehnite | 16 | 50.0 | 118 (SSD) | 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Redwood | 32 | 32.0 | 64 (SSD) | 3rd generation EPYC 7763v |
| Rhenium | 16 | 10.0 | 36 (SSD) | AWS Graviton2 Processor with 64-bit ARM Neoverse cores |
| Ruby | 16 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Sequoia v2 | 16 | 32.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation EPYC 7763v |
| Sequoia v2 1core | 16 | 32.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation EPYC 7763v |
| Sequoia v2 2core | 16 | 32.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation EPYC 7763v |
| Sequoia v2 4core | 16 | 32.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation EPYC 7763v |
| Siderite High Memory | 10 | 400.0 | 25 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Tantalum | 16 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Tenorite High Memory | 8 | 400.0 | 20 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Topaz | 30.5 | 25.0 | 56 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E7-8880 v3 (Haswell) |
| Tremolite | 64 | 100.0 | 59 | 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Tremolite Metal | 64 | 100.0 | 59 | 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Ice Lake) |
| Tsavorite | 14.2 | 100.0 | 98 (SSD) | Bare Metal - Intel Icelake |
| Yttrium | 10.66 | 100.0 | 164 (SSD) | Bare Metal - Intel Xeon Gold 6154 (Skylake) |
| Zinc | 15.25 | 25.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| High Clock-Rate (17) | ||||
| Andalusite | 8 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Aventurine | 16 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Caesium | 16 | 200.0 | 237 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Calyptolite | 4 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) |
| Diamond | 16 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8151 |
| Graphite V2 | 16 | 100.0 | 1250 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Skylake) processors |
| Hickory | 4 | 50.0 | 31 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa |
| Jacinth | 4 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Juniper | 5.33 | 100.0 | 16 | AMD EPYC (Rome) |
| Luna | 4 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Cascade Lake) |
| Luna Max | 4 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Cascade Lake) |
| Malachite | 16 | 50.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Moissanite | 8 | 50.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Prehnite | 16 | 50.0 | 118 (SSD) | 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (Ice Lake) |
| Pyrite | 8 | 100.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) Processors |
| Pyrite Max | 8 | 100.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) Processors |
| Tantalum | 16 | 200.0 | 36 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Large Disk (29) | ||||
| Albite | 28 | 200.0 | 120 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Caesium | 16 | 200.0 | 237 (SSD) | Intel Xeon 8375C (Ice Lake) with 200 Gbps low-latency inter-node communication |
| Calcite | 8 | 30.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8272CL (Cascade Lake) |
| Chromium | 15.75 | 30.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8272CL (Cascade Lake) |
| Chromium v2 | 16 | 35.0 | 32 (SSD) | 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Platinum 8370C (Ice Lake) |
| Cuprite | 32 | 400.0 | 150 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Cuprite High Memory | 59 | 400.0 | 150 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Diamond | 16 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8151 |
| Edenite | 14 | 200.0 | 60 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V73X (Milan-X) |
| Fluorite | 30.5 | 25.0 | 117 (SSD) | 16 nm Xilinx UltraScale Plus FPGA with Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Fordite | 16 | 400.0 | 75 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Fordite High Memory | 29 | 400.0 | 75 (SSD) | AMD EPYC Genoa X |
| Graphite | 15.25 | 25.0 | 475 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Graphite V2 | 16 | 100.0 | 1250 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Skylake) processors |
| Quartz | 15.25 | 20.0 | 400 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 (Ivy Bridge) |
| Melanite | 8 | 25.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175 (Skylake) |
| Melanite Max | 8 | 25.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175 (Skylake) |
| Moonstone | 16 | 25.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Moonstone Max | 16 | 25.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Pearl | 14 | 10.0 | 192 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5 v3 (Haswell) |
| Pyrite | 8 | 100.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) Processors |
| Pyrite Max | 8 | 100.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) Processors |
| Ruby | 16 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8175M (Skylake) |
| Spinel | 4 | 40.0 | 8 | Intel Xeon IceLake |
| Titanium | 8 | 25.0 | 80 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 (Haswell) |
| Topaz | 30.5 | 25.0 | 56 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E7-8880 v3 (Haswell) |
| Tsavorite | 14.2 | 100.0 | 98 (SSD) | Bare Metal - Intel Icelake |
| Yttrium | 10.66 | 100.0 | 164 (SSD) | Bare Metal - Intel Xeon Gold 6154 (Skylake) |
| Zinc | 15.25 | 25.0 | 40 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| GPU (22) | ||||
| Aquamarine v3 | 18.67 | 10.0 | 122 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2690 v4 (Broadwell) CPUs |
| Borate-1 | 8 | 25.0 | 56 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8259CL CPU |
| Borate-1 Lite | 8 | 25.0 | 62 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8259CL CPU |
| Borate-4 | 8 | 25.0 | 37 (SSD) | Intel Xeon Platinum 8259CL CPU |
| Celestine | 9.38 | 24.0 | 62 (SSD) | AMD EPYC w/ NVIDIA Ampere A100 |
| Citrine | 15.25 | 25.0 | 7 (SSD) | NVIDIA Tesla M60, Intel Xeon E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Cobalt V2 | 9.33 | 24.0 | 53 (SSD) | Intel E5-2690 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Dolomite | 15.25 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | NVIDIA V100-enabled w/ NVLink, Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| Grossular-1 | 8 | 100.0 | 112 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Grossular-1 8core | 8 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Grossular-4 | 8 | 100.0 | 158 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Grossular-8 | 8 | 100.0 | 79 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Iolite-1 | 7 | 32.0 | 45 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V12(Rome) |
| Iolite-4 | 7 | 32.0 | 45 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V12(Rome) |
| Mallorn | 9.17 | 24.0 | 93 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 7V13 w/ NVIDIA Ampere A100 |
| Obsidian | 30.5 | 25.0 | 37 (SSD) | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 (Haswell) |
| Raspite | 12.2 | 80.0 | 40 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 74F3V(Milan) CPUs |
| Raspite Half | 24 | 20.0 | 80 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 74F3V(Milan) CPUs |
| Raspite High Memory | 24.4 | 80.0 | 20 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 74F3V(Milan) CPUs |
| Raspite Sixth | 24 | 20.0 | 60 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 74F3V(Milan) CPUs |
| Raspite Third | 24 | 20.0 | 60 (SSD) | AMD EPYC 74F3V(Milan) CPUs |
| Rhodium | 15.25 | 25.0 | 37 (SSD) | NVIDIA V100-enabled w/ NVLink, Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2686 v4 (Broadwell) |
| GPU Rendering (4) | ||||
| Grossular-1 | 8 | 100.0 | 112 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Grossular-1 8core | 8 | 25.0 | 75 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Grossular-4 | 8 | 100.0 | 158 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Grossular-8 | 8 | 100.0 | 79 (SSD) | 2nd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Other (4) | ||||
| Clerite | 8 | 25.0 | 36 (SSD) | 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable (Cascade Lake) |
| Larch | 8 | 40.0 | 32 | 3rd generation AMD EPYC processors |
| Maple | 8 | 20.0 | 36 | AMD EPYC 7000 series |
| Sylvanite | 16 | 75.0 | 468 (SSD) | 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors (Ice Lake 8375C) |
Enhanced HPC Infrastructure Services
on the Largest Cloud HPC Network
The latest specialized architectures from leading cloud providers enhanced by Rescale’s unique job success guarantee. A range of options helps you balance flexibility, cost savings, and time-to-solve objectives.
Key Considerations For Hardware Selection
Businesses, on average, can increase workload performance by 30% and reduce overall simulation costs by 20% just by choosing a more optimal core type on Rescale.
Do you have a strategy to keep up with the latest technologies across all available across multiple providers?
Are you currently using the best cloud architectures for your specific workloads, optimized for cost, speed, or scale?
What metrics and data sources are you leveraging to maximize the performance and efficiency of your HPC and engineering resources?
Explore HPC Use Cases
Big Compute 2021 State of Cloud HPC Report
Download the Full Report High Performance Computing is a massive industry ($55 billion by 2024) that is the lifeblood of research and science innovation. From supersonic jets to developing cures for pandemics – research engineers rely on HPC for algorithmically complex workloads running on massive datasets. Today this HPC industry is still running mostly on-prem…
Nissan and Rescale: Innovation that Excites
Results About Nissan 85 Years of Innovation and Leadership Nissan is a global full-line vehicle manufacturer that sells more than 60 models under the Nissan, INFINITI and Datsun brands. In fiscal year 2018, the company sold 5.52 million vehicles globally, generating revenue of 11.6 trillion yen. Nissan’s global headquarters in Yokohama, Japan, manages operations in…