How CAE Simulations in the Cloud Are Driving Innovation
Research, engineering and product design are becoming increasingly complex and competitive. Cross-functional teams are under mounting pressure to move faster and faster. Rapid and successful product development depends on striking a balance between speed and thorough testing. Enter computer-aided engineering (CAE).
For decades, enterprises have relied on a combination of computer-aided design (CAD) and CAE simulations to guide product development. Where CAD uses software to create two-dimensional and three-dimensional drawings, CAE digitally represents these designs in a variety of real-world scenarios to predict and analyze their performance, safety, and production feasibility.
CAE makes it easier for research and development (R&D) teams to streamline costs, accelerate development cycles, and reduce the likelihood of product failures and recalls. CAE is also important for helping organizations become automation-ready given the rise of artificial intelligence.
Here’s a look into how CAE simulations fit into R&D workflows — and how organizations can benefit from moving their CAE projects into the cloud.
The Role of CAE Simulation in R&D: A Brief Overview
The first CAE simulations go back to the days of analog computing. During the 1960s, automakers first used CAE to solve differential equations for understanding vehicle dynamics. In the 1970s, NASA, Boeing, and others used CAE to understand the flight dynamics of rockets and aircraft.
In the decades following, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) took CAE a step further. CFD became a commercially adopted technique for producing “quantitative predictions of fluid-flow phenomena based on the conservation laws (conservation of mass, momentum, and energy) governing fluid motion,” according to Howard H. Hu.
Today, CAE simulations are a key part of engineering and design workflows. Examples include:
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Multibody Dynamics (MBD)
- Electromagnetics (EM)
- Manufacturing Process Simulation
- Multi-Disciplinary Design Optimization
- Acoustics and Vibrations
- Durability and Fatigue
- Crash and Impact Analysis
- Computational Chemistry
- Optics and Photonics
- Human Modeling and Simulation
Now, new technology advancements are making CAE even more effective, including:
- More robust and precise datasets
- More efficient computing infrastructure
- AI/ML predictive models and algorithms
- Integrations with complementary analysis systems
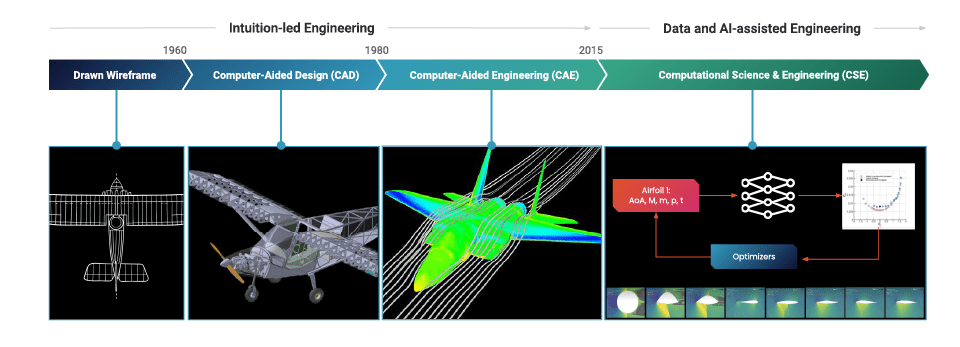
How CAE Simulations Work
CAE simulations simplify the process of predicting how design changes will alter product performance. As a result, the process of making improvements becomes more streamlined, leading to better products, lower development costs, and ultimately more satisfied customers.
CAE simulations are “consultative,” based on probabilities, rather than definitive fact. For this reason, CAE simulation interpretations currently require human judgment. A general trend is that CAE simulation model outputs have become more precise and predictable over the years. Building more trustworthy and true-to-reality models is crucial for the next generation of innovation.
This is where new artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies are helping improve CAE work.
A recent study from engineering.com “The Status and Future of Engineering Design and CAE Technologies” surveyed more than a hundred designers, engineers, managers, educators, and specialists. It found that “57% plan to apply their tools to artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions, 49% want to use them for generative design, and 46% are preparing to work on digital transformation.”
Challenges to Implementing CAE Simulations
Despite the availability of computing resources, organizations are struggling to keep pace with organizational expectations. According to the report, “A surprising 56% of respondents believe that they do not have adequate access to the latest and greatest tools, and less than half (44%) feel they have the best tools at their disposal to help them achieve their objectives.”
The biggest reason for these challenges was perceived accessibility to technology. Respondents in the report cited computational hardware limitations (29%), leadership alignment (28%), cybersecurity management (26%), and the challenge of staying proficient (21%) as being key barriers.
At one Analysis, Simulation, and Systems Engineering Software Summit (ASSESS) hosted by engineering.com, 41 executives identified the top challenges in managing and using CAE. These included:
- Design-centric workflows
- Ease of use and/or usability
- Analysis and simulation before CAD
- The impact of web, cloud, and mobile devices
- Capturing and reusing knowledge
- Systems approach to combining heterogeneous models
- Speed and model fidelity
- In-the-weeds technical issues
- Changes to licensing models
Fortunately, these are addressable challenges. New high performance computing-as-a-service (HPCaaS) technologies are bringing much needed help to computational researchers, engineers, and designers.
How Cloud HPC Is Making CAE More Effective
If engineers, designers, and other CAE simulation practitioners don’t have the best tools available, it’s unlikely that they are working to their full potential.
“Just as enterprise cloud computing created new ways for businesses to engage customers and disruptions from software-as-a-service to mobile computing, supercomputing will open up new possibilities for innovation breakthroughs by accelerating R&D speed and product development by orders of magnitude,” explains Joris Poort, CEO of Rescale in an article for Harvard Business Review “How Cloud-Based Supercomputing Is Changing R&D.”
Consider the case of Boom Supersonic, a startup (and Rescale customer) that is aiming to cut air travel time in half. The company is using HPCaaS to accelerate the many tiny decisions that culminate into big-picture strategic milestones.
Boom’s product development cycle is almost entirely simulation-driven, employing the Rescale platform from initial high-level concept down to the detailed design of items such as engine intakes. Using flight simulators, pilots are testing various flight conditions and helping refine requirements in a continuous loop with simulation.
“HPCaaS lets our team quickly disseminate simulation results to all the stakeholders in the process so that we can make rapid progress,” says Joshua Krall, co-founder and CTO of Boom. “This is a major benefit for a hard-tech startup like Boom as we work with a complex network of partners to launch an advanced, safety-critical product that needs to work the first time exactly as designed and simulated.”
Beyond accelerating time-to-market and creating a digital twin to navigate constraints to physical prototyping, there are substantial cost advantages to moving CAE simulation workflows to the cloud.
Consider the scenario of Brother Industries, which utilizes HPCaaS for an enhanced design environment in the cloud. Its simulation environment for impact analysis and other efforts has been moved to the cloud to increase design agility.
“When weighing the benefits of either using budget to replace internal servers or moving to a cost-effective cloud environment with high processing speeds, the decision was clear,” says Masahito Nakagiri, an IT supervisor at Brother Industries. “The cloud also has the advantage of business continuity in the event of a disaster.”
Reinforcing Engineering Decisions to Accelerate Innovation
The key to successful R&D is in the empowerment of decision-making throughout the organization. With the right tools, anything is possible. And the sooner teams can explore options and answer questions about the implications of design ideas, the quicker they can invent and improve products.
The ability to arrive at answers sooner is mission-critical to accelerating the pace of innovation. Faster CAE simulations lead to smoother handoffs between teams, a higher degree of confidence in testing, and ultimately better and safer products that improve lives.
If you would like to learn more about Rescale’s platform, please sign up for a demo or contact us.